Shoulder Replacement
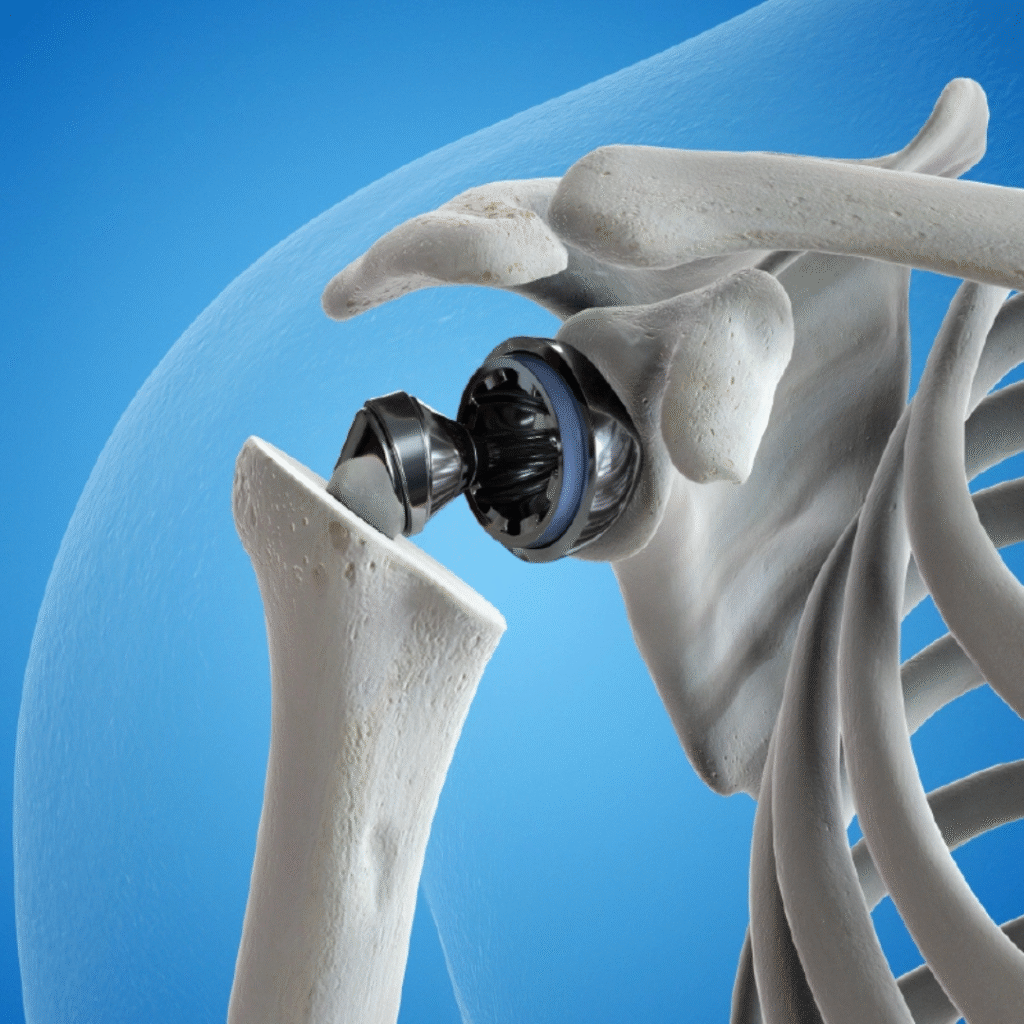
Shoulder Replacement
Shoulder replacement (also called shoulder arthroplasty) is a surgical procedure in which the damaged parts of the shoulder joint are replaced with artificial components. It is usually recommended when the shoulder joint is severely damaged by arthritis, injury, or other conditions that cause pain and limit movement.
By replacing the worn-out surfaces with smooth artificial implants, shoulder replacement helps restore function, reduce pain, and improve quality of life.
Causes / Conditions Leading to Shoulder Replacement
Severe Osteoarthritis
Wear-and-tear arthritis that damages the cartilage in the shoulder joint.Rheumatoid Arthritis
An autoimmune condition causing chronic joint inflammation and damage.Post-Traumatic Arthritis
Arthritis that develops after an injury, fracture, or previous surgery.Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy
Severe arthritis combined with large, long-standing rotator cuff tears.Severe Fractures
Complex fractures of the upper arm bone (humerus) that cannot be repaired.
Symptoms Requiring Shoulder Replacement
Persistent shoulder pain that does not improve with medications or physiotherapy
Stiffness and reduced range of motion
Weakness or difficulty lifting the arm
Grinding, catching, or locking sensation in the joint
Pain that interferes with daily activities and sleep
Diagnosis
Medical History
Assessment of symptoms, duration of pain, and effect on daily activities.Physical Examination
Evaluation of joint stability, motion, and strength.Imaging Tests
X-rays to check joint space, bone damage, or deformity
MRI/CT scans (if needed) to assess cartilage, ligaments, and rotator cuff condition
Types of Shoulder Replacement
Total Shoulder Replacement
Both the ball (humeral head) and socket (glenoid) are replaced with artificial components.Partial Shoulder Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty)
Only the ball of the upper arm bone is replaced.Reverse Shoulder Replacement
The positions of the ball and socket are switched, often used in patients with severe rotator cuff damage.
Treatment & Recovery
Surgery
Damaged bone and cartilage are removed and replaced with metal and plastic implants designed to mimic natural joint movement.Rehabilitation
Recovery is guided through physiotherapy, usually in phases:0–2 Weeks – Sling support, pain management, and gentle exercises.
2–6 Weeks – Begin passive and assisted range-of-motion therapy.
6–12 Weeks – Gradual strengthening and improved mobility.
3–6 Months – Return to normal daily activities, with sports after medical clearance.
Benefits of Shoulder Replacement
Pain Relief – Significant reduction in chronic shoulder pain.
Improved Mobility – Restores range of motion and strength.
Better Quality of Life – Allows return to daily activities, work, and recreational sports.
Long-Lasting Results – Implants often last 15–20 years with proper care.

